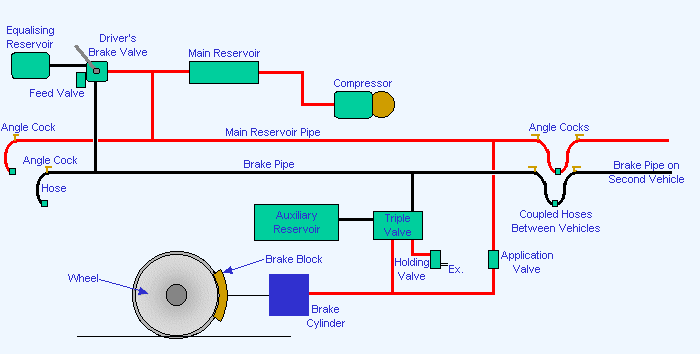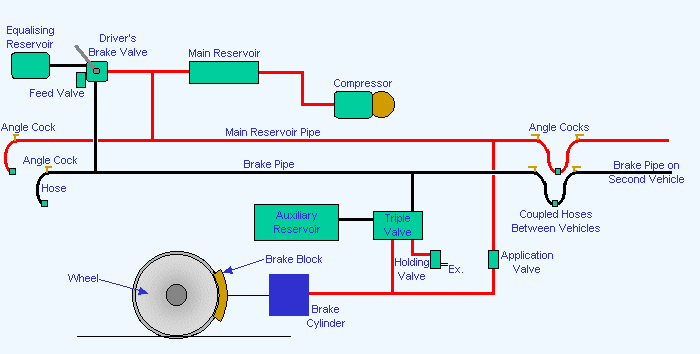
1. How does an air braking system in a car work?
An air braking system in a car, also known as an air-over-hydraulic braking system, works by transmitting brake actuation force from the brake pedal to the brake components using compressed air.
When the driver presses the brake pedal, air from the compressor in the engine compartment is directed into an air storage tank. This compressed air is then sent through hoses and valves to the brake chambers which are attached to the brake shoes or the brake calipers.
The brake chamber converts the air pressure into linear force on the push rod, which moves the brake shoes apart or applies hydraulic pressure on the brake calipers. This action causes the brake pads or shoes to press against the wheels, slowing the vehicle down.
The air braking system also includes other components such as the air dryer, air compressor, relay valves, brake lines, brake control valves, and brake drums or rotors.
Overall, the air braking system provides an efficient, reliable, and consistent way to stop a car, making it a popular choice in heavy-duty vehicles such as trucks and buses.
SuBy implementing these tips, you can help improve the efficiency of your air braking system, avoid costly repairs and maintenance, promote safety and enjoy better braking performance.
2. What are the components of an air braking system in a car?
An air braking system in a car consists of the following components:
1. Brake pedal – used by the driver to apply the brakes
2. Air compressor – generates compressed air that powers the system
3. Air storage tanks – stores compressed air for future use
4. Air dryer – removes moisture from the compressed air
5. Air hoses – carries the compressed air to other components
6. Relay valves – controls the flow of air to the brake chambers
7. Brake chambers – convert air pressure into linear force on the brake components
8. Brake lines – carries brake fluid to hydraulic brake components
9. Brake control valves – regulates brake pressure to optimally control braking
10. Brake drums or rotors – used to slow the spinning wheels of the vehicle
These components work together seamlessly to help ensure optimal safety and braking performance.
3. What are some common problems with an air braking system in a car?
Some common problems that can occur with an air braking system in a car include:
1. Air leaks – one of the most common issues is air leaks, which can be caused by worn hoses, faulty valves, or damaged seals. Leaks can cause a reduction in the effectiveness of the brakes.
2. Brake fade – this occurs when the brakes overheat and lose their effectiveness, which can be caused by excessive use or continuous and prolonged braking.
3. Contamination of brake fluid – if the brake fluid is contaminated, it can damage the rubber seals and hoses in the air braking system, causing it to fail.
4. Worn brake pads or shoes – worn pads or shoes can cause the brake components to wear out more quickly, reducing their effectiveness.
5. Faulty valves – problems with the valve assembly, like sticking valves or faulty governor valves, can cause brake loss.
6. Malfunctioning compressor – a malfunctioning compressor can cause uneven air pressure in the system, leading to ineffective braking.
If you notice any of these problems with your air braking system, it’s important to have it inspected and repaired as soon as possible by a professional technician to prevent further damage or potential safety issues.
4. How can you tell if your air braking system needs maintenance?
Here are a few signs that may indicate that your air braking system needs maintenance
1. An illuminated warning light – if the brake warning light on your dashboard comes on, it may indicate low air pressure in the system, indicating a possible leak.
2. Brake pedal feels spongy – if the brake pedal feels spongy or unresponsive, it may indicate air in the system or worn brake pads or shoes.
3. Unusual noises – if you hear any strange noises, such as hissing, grinding, or squealing while applying the brakes, it may indicate a problem with the system.
4. Longer braking distance – if it takes longer to stop the vehicle than usual, it may indicate a problem with the brake pads or shoes, a leak in the system, or a malfunctioning valve.
5. Uneven braking – if one wheel or set of wheels is braking more effectively than the others, it may indicate a problem with the brake components in that area.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to have your air braking system inspected by a professional technician as soon as possible. Regular maintenance can help prevent these issues from developing, and can ultimately help you keep your air braking system working properly and safely.
5. How often should you get your air braking system serviced?
The recommended service interval for an air braking system in a car can vary depending on several factors, such as the manufacturer’s recommendations, the mileage on the vehicle, the type of driving conditions, and the severity of use.
In general, it’s recommended to have the air braking system inspected and serviced regularly, typically every six months to one year. During these services, the technician will check for any signs of leaks, wear, or other damage, and perform any necessary repairs or maintenance.
Keep in mind that heavy-duty vehicles such as trucks and buses may require more frequent inspections and servicing due to the high demands placed on the air braking systems.
It’s also important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your specific vehicle, and to have the air braking system inspected and serviced immediately if you notice any signs of problems or irregularities.
Overall, regular servicing of your air braking system can help prevent major issues from developing, and can help ensure optimal safety and performance while driving.
6. What are some tips for maintaining your air braking system?
Here are some tips for maintaining your air braking system:
1. Inspect the system regularly – Regular inspections of the air braking system can help identify and address any issues early and prevent them from turning into major problems.
2. Check the air pressure – Ensure that the air pressure in the system is at the recommended level to ensure optimal brake efficiency.
3. Keep the air dry – Moisture in the air can damage the air braking system components, including the brake chambers, air hoses, and valves. Use a good quality air dryer to ensure that the air remains dry before it enters the system.
4. Service and replace filters – Replace air filters as per recommended intervals or when they become dirty or clogged.
5. Use the correct type of brake fluid – Use the type of brake fluid recommended by the vehicle’s manufacturer to ensure maximum efficiency of brake components.
6. Regularly service the compressor – Regularly service the air compressor to prevent it from malfunctioning and causing uneven air pressure in the system.
7. Drive safely – Avoid sudden or excessive braking as it can cause excessive heat, wear, and premature failure of the brake components.
By following these tips, you can help maintain the efficiency of your air braking system and ensure safer driving on the road.
Car trouble shooting
7. How can you troubleshoot common air braking problems in a car?
Here are some steps you can take to troubleshoot common air braking problems in a car:
1. Check the air pressure – Ensure that the air pressure in the system is sufficient and proper. Low air pressure can reduce the efficiency of the brakes.
2. Check for air leaks – Identify air leaks in the hoses, fittings, and valves. Listen for any hissing or whistling sounds while the air system is pressurized.
3. Check the brake pads and shoes – Inspect the brake pads and shoes for excessive wear or damage. Worn brake pads can cause uneven braking or loss of braking power.
4. Inspect the compressor – Check if the compressor is working as it should be. A malfunctioning compressor can cause uneven pressure in the air system.
5. Check the valves – Ensure that the valves are working correctly, and check for any blockages or sticking.
6. Check for contamination in brake fluid – Contaminated or dirty brake fluid can cause damage to seals and other components of the air braking system.
7. Check for excessive brake heat – Overuse or continuous braking can heat up the brake components excessively, resulting in brake fade.
If you are not confident in troubleshooting the air braking system yourself, it’s recommended to have a professional technician inspect and repair the system for you. A professional technician can efficiently diagnose and repair any issues with the air braking system.
8. What are some safety precautions to keep in mind when dealing with an air braking system in a car?
When dealing with an air braking system in a car, it’s important to take the following safety precautions:
1. Wear protective gear – Always wear protective gear like gloves and safety glasses to prevent contact with harmful chemicals and sharp metal parts.
2. Safe parking – Always park the car on level ground and engage the parking brake before working on the air braking system.
3. Turn off the engine – Before working on the air braking system, turn off the engine and let it cool down to prevent burns or injuries.
4. Discard used parts properly – Dispose of used brake pads, shoes, or hoses safely and properly.
5. Follow manufacturer instructions – Always follow the manufacturer instructions for maintenance and repair of the air braking system. Avoid tampering, modifying or repairing the system unless you are trained or have adequate knowledge to properly service it.
6. Avoid excessive use – Avoid excessive or continuous use of the brakes, which can cause excessive heat buildup and lead to brake fade and reduced efficiency of the braking system.
7. Get professional help – If you’re uncertain about how to maintain or repair your air braking system, always get professional help to prevent injury or damage to your vehicle.
By practicing these safety precautions when dealing with an air braking system in a car, you can help ensure a safer environment for you and others around you.
9. What are the differences between air brakes and hydraulic brakes in a car?
The main differences between air brakes and hydraulic brakes in a car are:
1. Working principle – Air brakes use compressed air to convert brake actuation force, while hydraulic brakes use hydraulic fluid.
2. Components – Air brakes use air compressors, air storage tanks, and brake chambers, while hydraulic brakes use master cylinders, brake hoses, and brake calipers or wheel cylinders.
3. Efficiency – Air brakes are more efficient than hydraulic brakes in heavy-duty vehicles like trucks and buses as they can handle larger loads and offer better control.
4. Durability – Air brake systems are more durable than hydraulic brake systems, as they have fewer moving parts and are resistant to corrosion, resulting in reduced need for maintenance, repairs, or replacements.
5. Cost – Air brake systems are more expensive to install and maintain than hydraulic brake systems, as they require additional components such as air compressor and storage tanks.
Air brakes deliver superior stopping power, making them the more popular choice in large vehicles with heavy loads, while hydraulic brakes are commonly used in smaller personal vehicles.
10. How can you improve the efficiency of your air braking s
1. Keep the air dry – Moisture in the air can cause damage to components like the brake chambers, valves, and air hoses. Use a good quality air dryer to ensure that the air remains dry before it enters the system.
2. Maintain proper air pressure – Ensuring proper air pressure is critical for optimal braking efficiency. Check the air pressure regularly as a low amount of air pressure can decrease the efficiency of the brakes.
3. Replace brake pads and shoes regularly – Worn brake pads can reduce the efficiency of your braking system. Inspect the brake pads and shoes regularly and replace them as required.
4. Service the compressor regularly – Regular servicing of the air compressor can help maintain good air pressure and overall system efficiency.
5. Keep the system free from contaminants – Contaminants such as oil or grease can damage the rubber seals and other components in the system, thereby reducing overall efficiency.
6. Avoid overuse – Avoid sudden or excessive braking as it can cause excessive heat, wear, and premature failure of the brake components, thus reducing the efficiency of the braking system.
Here are some common air braking system faults, their causes, and remedies:
1. Air leak – Leaks in the air brake system can result in a loss of pressure and poor brake performance. Common culprits include damaged hoses or fittings, faulty valves, or worn diaphragms.
Remedy: Locate the source of the leak and replace the affected component(s).
2. Brake fade – Brake fade occurs when the brakes lose stopping power due to overheating of the brake components, such as brake drums or rotors, or worn-out brake pads or shoes.
Remedy: Allow the brakes to cool down and adjust or replace worn-out parts.
3. Uneven braking – Uneven braking can occur when the brakes on one wheel set engage earlier or more forcefully than the others, leading to the vehicle pulling to one side or the other during braking.
Remedy: Inspect the brake system and adjust or replace components as needed to ensure even braking across all wheels.
4. Spongy brakes – Spongy brakes occur when there is air in the brake system, resulting in a soft and unresponsive feel when the brake pedal is pressed.
Remedy: Bleed the brake system to remove air pockets. If necessary, replace the brake fluid, ensuring the fluid level is at the appropriate level.
5. Brake drag – Brake drag happens when the brake pads or shoes fail to release fully, creating friction between the brake components and the rotor or drum.
Remedy: Back off the adjustment on affected brake components and check that the components are correctly installed and lubricated. In severe cases, it may be necessary to replace the affected part.
6. Brake chamber failure – Brake chamber failure occurs when the diaphragm inside the brake chamber ruptures or becomes damaged.
Remedy: Replace the affected brake chamber with a new one.
In conclusion, regular maintenance, inspection, and repairs of the air braking system are critical to avoid or fix faults that could lead to brake failure or less efficient braking.
AN ELECTRONIC AIR BRAKING SYSTEM
Operations of an electronic air braking system
An electronically controlled air brake uses electronic control units to manage the brake system’s air pressure, instead of relying entirely on traditional mechanical control valves. The operating principle of an electronically controlled air brake is to provide precise and consistent control of the brake system’s pressure, resulting in improved safety, reliability, and efficiency.
In this system, various sensors and electronic modules monitor the vehicle’s behavior, speed, and other relevant parameters, which then communicate with the control unit to regulate the air pressure supplied to the brakes.
When the driver operates the brake pedal, a signal is sent to the electronic control unit, which calculates the desired brake force based on the input and existing conditions, such as the vehicle’s speed and load.
The electronic control unit then activates the solenoid valve, which controls the airflow of the compressed air. Electronic signals are then sent to the brake actuators to engage the brake system accordingly – either partial or full brake application.
The electronic control unit periodically adjusts the brake pressure to ensure maximum control and ensure smooth stops without the risk of skidding or sliding. In addition, the electronic control unit can also account for other variables, such as brake temperature and wear, to optimize braking performance.
Overall, the electronic control unit in an electronically controlled air brake system allows for more precise and efficient control of the brake system, resulting in improved safety and performance.
Brake adjustment
Enctioning correctly and effectively. Here is a step-by-step guide on how brake adjustment is carried out in an air braking system:
1. Park the vehicle on a level surface – Before proceeding with the brake adjustment, ensure that the vehicle is parked on a level surface. This ensures that there is enough pressure in the brake chambers and that there are no obstructions that could interfere with the adjustment process.
2. Release the brakes – Release the brakes by opening the brake lines. This ensures that there is no air pressure in the brake chambers, allowing the pushrods to move freely.
3. Adjust the brake shoe clearance – Rotate the slack adjuster to adjust the brake shoe clearance. The slack adjuster is a component that connects the pushrod to the brake shoes. Rotating the slack adjuster either increases or decreases the clearance of the brake shoes against the brake drums.
4. Check that the pushrod travel is adequate – After adjusting the brake shoe clearance, check that the pushrod travel is adequate. This means that there should be enough movement in the pushrod when the brake pedal is depressed to engage the brakes effectively.
5. Reapply the brakes – Reapply the brakes by closing the brake lines. This will build pressure in the brake chambers, and the brakes should engage as soon as the brake pedal is pressed. Check that the brakes engage adequately and that there is no binding or dragging.
6. Conduct a road test – After adjusting the brakes, carry out a road test to ensure that the brakes are functioning correctly. Test the brakes at various speeds and note any unusual braking behavior, such as drifting or pulling to one side.
7. Conduct periodic brake adjustments – Brake adjustment in an air braking system should be carried out periodically, typically after every 10000 miles of driving or as recommended by the manufacturer. This ensures that the brake system remains effective and reliable over time.
Thus, regular brake adjustment is crucial in ensuring the safety and efficiency of an air braking system in a vehicle.
What is the function of the air brake actuators
The air brake actuator, also known as the brake chamber, is an essential component of an air braking system in a vehicle. It is attached to the brake shoes in drum brakes or brake pads in disc brakes. The actuator operates by converting the compressed air generated by the system into mechanical force to engage the brakes.
The function of the air brake actuator is to transmit the air pressure from the air braking system to the brake shoes or pads, creating the necessary force to engage the brake mechanism and slow down or stop the vehicle.
When the driver steps on the brake pedal, the compressed air is channeled to the brake chambers, pressurizing the diaphragms within. This pressure then acts on the actuator’s pushrod, which in turn pushes the brake shoes or pads against the brake drum or disc.
The actuator brings about the necessary force to apply the brakes, creating friction of the shoes against the drum or pads against the disc. The brake force produced then slows down or stops the vehicle.
After releasing the brake pedal, the compressed air is released, and the actuator’s diaphragms return to their original position, pulling back the pushrod and releasing the brake shoes or pads, allowing the vehicle to move freely.
Thus, the air brake actuator plays a critical role in the air braking system of the vehicle, providing the force required to engage the brakes and bring the vehicle safely to a stop.
What is the function of the pressure regulating valve
The pressure regulating valve, also known as a brake relay valve, is a critical component of an air braking system in a vehicle. It is usually located between the foot-operated brake valve and the brake chambers and regulates the pressure between the two.
The primary function of the pressure regulating valve is to ensure that the air pressure supplied to the brake chambers is within safe limits. It regulates the pressure by decreasing the air pressure between the foot-operated brake valve and the chambers to a safe and suitable level.
When the driver steps on the brake pedal, the foot-operated brake valve sends compressed air to the brake relay valve. The pressure regulating valve then functions as a regulator, reducing the air pressure supplied to the brake chambers and keeping it within a safe operating range. The brake chambers then receive the regulated pressure and activate the brake shoes accordingly.
In addition to regulating the pressure, the pressure regulating valve also performs other functions such as ensuring that brake pressure is equalized across all the brake chambers and preventing air pressure surges that could result in brake lock-ups.
The pressure regulating valve is crucial in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of the braking system. It ensures that the brakes are not over-pressurized, preventing premature wear of brake components and improving the overall efficiency of the system.
What is the function of the foot-operated brake valve
The foot-operated brake valve is an essential component of an air braking system in a vehicle. It is commonly known as the brake pedal or the foot valve. The brake valve controls the braking system within the vehicle, allowing the driver to apply or release the brakes as needed.
The primary function of the foot-operated brake valve is to convert the driver’s input force (as exerted on the brake pedal) into air compressor pressure, which in turn activates the brakes. The brake valve determines the amount of air that is released into the air-operated brake system when the driver depresses the pedal.
When the driver applies the brake pedal, the foot valve opens, releasing compressed air from the system’s reservoir, which in turn forces the brake chambers to close around the brake shoes, creating friction with the brake drum or disk, slowing down or stopping the vehicle.
When the driver releases the brake pedal, the foot valve closes off any air supply to the brake chambers, releasing the brakes, and allowing the vehicle to move freely.
Thus, the foot-operated brake valve acts as a crucial interface between the driver and the braking system, enabling safe and effective braking of the vehicle. It responds to the driver’s input, regulating the flow of air from the compressor to the brakes, ensuring reliable and consistent braking performance.
Discuss the safety test carried out on the air braking system
Safety tests are conducted on an air braking system to ensure that the system is functioning properly and to prevent accidents resulting from brake failure. Here are the common tests carried out on air braking systems to ensure safety:
1. Leakage tests – Leakage tests are carried out to check for any leaks across the entire braking system. Any leaks reduce the air pressure in the system, causing brake failure. Leaks can be detected using approved leak detection methods.
2. Load valve pressure tests – This test ensures that the load pressure limit for a particular vehicle make and type is met before the system automatically releases the pressure. It also ensures that the load signal indicator light and valve are functional.
3. Operational tests – This test checks the function of the brake system and ensures that it’s responding correctly to the given braking signal from the driver. This test is carried out in a safe area and examines the braking distance and its effectiveness while under normal operating conditions.
4. Emergency stop capability tests – The emergency stop capability test determines the stopping distance and time required to stop the vehicle in an emergency. It also checks the performance and reaction time of the braking system when subjected to emergency situations.
5. Performance tests – Performance tests involve evaluating the overall performance of the braking system to ensure that it meets set standards. The test includes the brake application time, braking force, and control.
These tests ensure that the braking system and its components are properly functioning and safe for use, ultimately reducing the risk of accidents and injuries that come from brake failures. Brake systems should be tested at regular intervals to ensure continuous safety.
What is the function of a gorvrnor valve as applied to air braking system
A governor valve is a critical component in an air braking system and performs an essential function to maintain the air pressure in the system. The governor valve maintains the air pressure in the air reservoir at a safe and continuous operating level by controlling the operation of the air compressor.
The governor valve is typically located close to the air compressor of the air braking system and adjusts the amount of air that enters the system’s air tanks. The governor valve works by monitoring the air pressure in the system’s tank and controlling the compressor’s operation to ensure that a set minimum pressure is always maintained.
When the air pressure in the reservoir begins to drop below a specified level(as a result of prolonged brake usage), the governor valve signals the air compressor to begin working, thereby increasing the pressure in the system’s air tanks. As the air pressure rises to the upper limit, the governor valve stops the compressor from overloading the pressure up to an unsafe level.
Thus, the primary function of a governor valve is to maintain safe and steady air pressure in the air braking system, ensuring stable and reliable braking performance of the vehicle.
AIR COMPRESSOR
The function of air compressor
The function of an air compressor is to compress air and convert it to mechanical energy, which can be used to power various pneumatic tools and systems, including air brakes in a vehicle. Air compressors work by pulling in air from the surroundings and compressing it by reducing its volume. The compressed air is then stored in a tank or reservoir, which can then be used to power air tools or air brakes.
In an air braking system, the air compressor is responsible for compressing air and sending it to the storage tanks. It is driven by the engine of the vehicle or can often be powered by its own electric motor. Compressed air from the reservoir is then used to power the brake chambers, which in turn activate the brake shoes and linings. Without the air compressor, the air brakes system would not function, and braking would be ineffective.
Thus, the air compressor plays a critical role in air braking systems by supplying compressed air to power the brakes, ensuring the safety and efficiency of heavy-duty vehicles on the road.
Advantages of air braking system
Sure, here are some advantages of an air braking system in a vehicle:
1. More effective braking power – Air brakes offer superior stopping power compared to hydraulic brakes, making them especially suitable for large vehicles and heavy loads.
2. Enhanced safety – Air brakes provide quicker and more efficient braking performance, reducing the likelihood of accidents and enhancing the overall safety of the vehicle.
3. Durability – Components of air braking systems are designed to withstand harsh working environments, high demands, and heavy use, making them more durable compared to hydraulic braking systems.
4. Easy to repair and maintain- Air brakes have fewer moving parts and are easier to diagnose and repair, reducing maintenance costs and downtime of the vehicle.
5. Better control – Air brake systems offer better control as the driver can adjust the amount of pressure applied to the brakes, reducing the risk of skidding or sliding.
6. Reduced brake fade – Air braking systems are less prone to brake fade, as they are less susceptible to overheating or wearing down under heavy use.
7. Better fuel economy – Vehicles equipped with air braking systems may yield better fuel economy as the brakes require less mechanical energy to function.
Overall, air braking systems offer several advantages over hydraulic braking systems in terms of performance, safety, durability, and efficiency, especially in heavy-duty vehicles and situations requiring high braking power.